Chromatography is a technique for separating mixtures into their components in order to analyze, identify, purify, and/or quantify the mixture or components.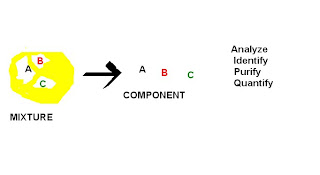
Chromatography is used by scientists to:
• Analyze – examine a mixture, its components, and their relations to one another
• Identify – determine the identity of a mixture or components based on known components
• Purify – separate components in order to isolate one of interest for further study
• Quantify – determine the amount of the a mixture and/or the components present in the sample
Detailed Definition:
Chromatography is a laboratory technique that separates components within a mixture by using the differential affinities of the components for a mobile medium and for a stationary adsorbing medium through which they pass.
Terminology:
• Differential – showing a difference, distinctive
• Affinity – natural attraction or force between things
Definition of Chromatography
Simplified Definition:
Chromatography separates the components of a mixture by their distinctive attraction to the mobile phase and the stationary phase.
Explanation:
• Compound is placed on stationary phase
• Mobile phase passes through the stationary phase
• Mobile phase solubilizes the components
• Mobile phase carries the individual components a certain distance through the stationary phase, depending on their attraction to both of the phases
